In Vitro Fertilisation is a process of fertilizing an egg with sperm –in vitro– in a laboratory setting to obtain fertilized embryos that will be placed into the woman’s uterus where they will develop resulting in pregnancy.
What is In Vitro Fertilization?
IVF is a kind of a sophisticated assisted reproductive treatment. During the IVF procedure an egg is fertilized with a sperm sample in a laboratory –in vitro. Thus, it is possible to obtain high-quality embryos, which are likely to result in pregnancy once transferred to the patient’s uterus.
To procure the eggs for the IVF procedure the patient is required to undergo a controlled hormonal stimulation. These eggs are fertilized in a laboratory setting (in vitro) and stay under supervision for a few days to let them develop. Out of this number of embryos only one is transferred back into the uterus while the others are stored frozen to be used in the future.
When is it used?
The IVF procedure may be performed with the use of a donated sperm sample or sperm from the patient’s partner. Thus, fertilization is not hindered by factors that would have affected the natural process. In vitro fertilization is recommended for:
Women after several failed attempts at artificial insemination. Women diagnosed with advanced endometriosis, probably affecting the fallopian tubes and the quality of oocytes. Women of advanced maternal age with a decrease in the quality of oocytes. Women who have damaged fallopian tubes or have none at all. Women suffering from hydrosalpinx. Couples who present a case when it is essential to perform a Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis. Couples where the male partner’s sperm is of poor quality (moderate or severe male factor infertility).
Success rates
IVF is proven to be more efficient than simple assisted reproductive procedures, for example, timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination. An accredited body (RAHR) carries out a yearly audit of our pregnancy rates. Many factors influence the probability of pregnancy: medical and reproductive history, age, ovarian reserve, and more. We can be sure of one thing at GENESIS — the treatment prescribed by our fertility specialists will be the most professional and personalized and with the use of the most advanced technology. This will lead us to our goal — your pregnancy.
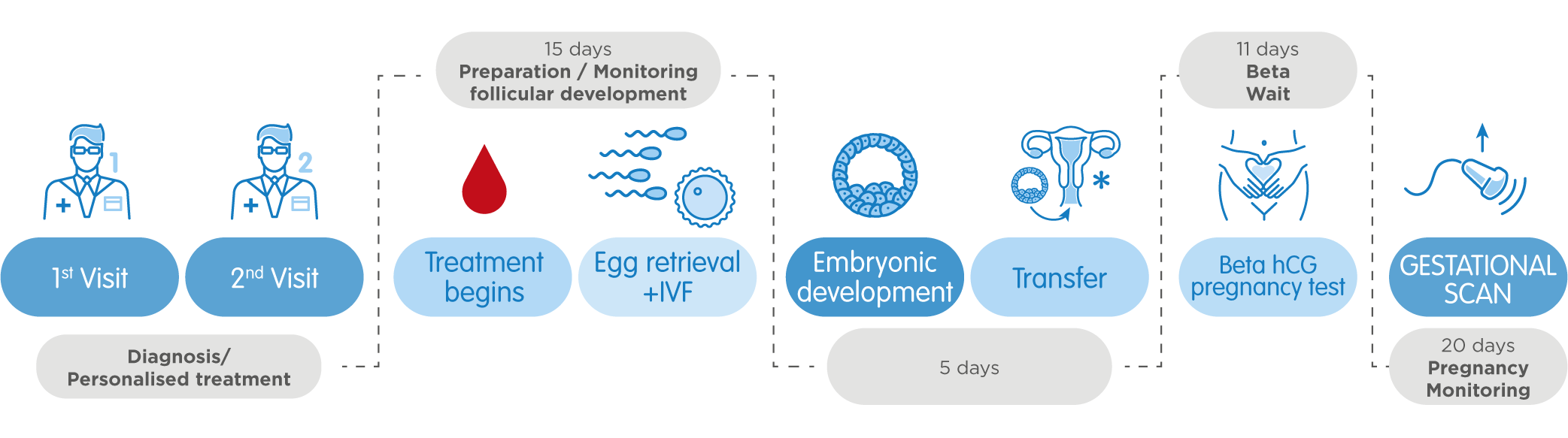
First visit
The treatment procedure starts with you visiting any GENESIS clinic where you will have a consultation with our specialist. After a careful analysis of your medical record and all the available information on the prior treatments you will receive a diagnosis. This appointment also involves a full gynaecological examination and a sperm analysis if you intend to use your partner's biological material. Making sure that the diagnosis is personalised, GENESIS is capable of providing the patients with a treatment best suited to their needs.
Ovarian stimulation
When the patient returns home, she makes a start on the ovarian stimulation by administering daily injections on her own or with the assistance of a nurse. One natural menstrual cycle results in only one egg, though this 15-25 days special hormonal treatment stimulates multifollicular growth producing several oocytes. Later they will be fertilized and once developed into embryos they are sorted by quality. One will be transferred into the patient’s womb, the rest are stored frozen to be used in future.
You will have multiple ultrasound scans (3 or 4) and blood tests performed by your gynaecologist in the course of the procedure to control the stimulation. Once the follicles reach the necessary size and quantity, you will be administered a dose of the hCG hormone to prompt oocyte maturation. The procedure of oocyte retrieval will be scheduled 36 hours later at your GENESIS clinic.
Egg collection
The procedure is fairly simple: 15-20 minutes in an operating room, and you will be sedated so as not to feel any discomfort.
The ovaries are accessed via the vaginal cavity where we
puncture every follicle. The oocytes are contained in the fluids aspirated from the follicles. Later the eggs will be fertilized in vitro in the laboratory.
The patient should have some rest after the procedure and may be discharged afterwards to carry on with the daily activities.
In vitro fertilization
Fertilizing the oocytes with donor’s or partner’s sperm in vitro is the next step of the IVF.
This procedure has two approaches: conventional IVF that simulates the natural fertilization process by placing each egg in a culture plate with previously manipulated sperm; and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). The latter is a high-precision method which consists of selecting the sperm cells of the highest quality and microinjecting them one by one into each of the oocytes.
Embryo culture
The embryo culture takes 5 to 6 days, and during this time the patient may choose to return to her home country. Embryologists at our clinic take it upon themselves to create stage-specific culture conditions crucial for the embryo development. At the same time, the specialists monitor and analyse the embryo development in order to assess the quality. Moreover, due to the time-lapse technology, we can monitor all the aspects of the process in real time. This allows for better quality assessment in terms of morphological criteria, and also brings to light other features related to oocyte viability and times of division. Thus, we are capable of collecting valuable data that allows us to discard the embryos that deviate from correct evolution and are unlikely to induce pregnancy.
Transfer of the best embryo
The patient’s uterus must undergo preparation before the oocyte transfer, making sure that the endometrium (the inner layer of the uterus) is of the proper thickness for the embryo which will most likely lead to pregnancy.
The transfer will be performed at the same GENESIS clinic where the retrieval took place. With the help of a cannula the best quality embryo will be transferred into the patient’s womb. The procedure is quick and painless and will be performed in an operating room. The embryo transfer is done outpatiently and requires no anesthesia.
Vitrification of the remaining embryos
All the remaining high-quality embryos undergo the process of vitrification (cryopreservation) to be used in the future, making a second cycle of ovarian stimulation redundant.
Pregnancy test
After the patient is safely at home, our specialist will recommend the approximate date for a blood pregnancy test, that is usually 11 days after the transfer. The patient may carry on with the usual daily routine at this point, though we recommend laying off the high-intensity activities. In case of a positive outcome, the patient will have her gynaecologist take a control ultrasound scan 20 days later. This will serve as a basis for GENESIS to discharge you and let you proceed with your pregnancy under the supervision of your local doctor or midwife.